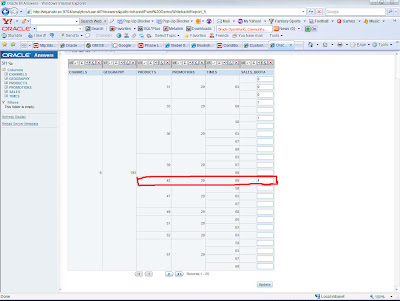
I had covered an approach here to do write backs into Essbase from BI EE. In some cases that approach would be sufficient. But in most of the cases, end users would want the capability to do a bulk write back similar to the default write back option provided by BI EE(like in relational sources). For example, if you look at the screenshot below, we have an Essbase report containing Q1, Eastern Market sales.

If you use the last blog entry’s approach you can write back to Essbase one row at a time. But what if our requirement is to write all the modified rows in a single shot to Essbase. In order to achieve that, the architecture for write back would be slightly different from what we saw before. The high level architecture is given below

As you see, in order to achieve the writebacks we would be using the usual Write back template provided by BI EE. The main difference between this and the relational write back is the fact that we would be writing into a global temporary table. We are using a Global Temporary table as it has the feature of truncating itself at the end of a transaction or a session. This Global Temporary table is used just for dummy purpose. During the insert into the temporary table, we would be calling a function which would in turn pass down the parameters to the UTL_HTTP function to call the custom JSP that we created last time. So let us first start with the JSP page that we had created before. For the sake of completeness, i am pasting the code again here.
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=windows-1252"%><%@ page import="java.io.*" %><%@ page import="java.util.Map" %><%@ page import="java.util.Map.Entry" %><%@ page import="java.util.jar.Attributes" %><%@ page import="java.util.Iterator" %><%@ page import="com.essbase.api.base.*" %><%@ page import="com.essbase.api.dataquery.*" %>
<%@ page import="com.essbase.api.session.*" %>
<%@ page import="com.essbase.api.datasource.*" %>
<%@ page import="com.essbase.api.domain.*" %>
<%@ page import="com.essbase.api.metadata.*" %> <%="WriteBack Started" %><%
String s_userName = "admin";
String s_password = "password";
String s_olapSvrName = "localhost";
String s_provider = "http://localhost:13080/aps/JAPI";
try
{
IEssbase ess = IEssbase.Home.create(IEssbase.JAPI_VERSION);
IEssDomain dom = ess.signOn(s_userName, s_password, false, null, s_provider);
IEssOlapServer olapSvr = (IEssOlapServer)dom.getOlapServer(s_olapSvrName);
olapSvr.connect();
IEssCubeView cv = dom.openCubeView("Data Update Example",s_olapSvrName, "Demo", "Basic");
String v_Market = request.getParameter("p_Market");
String v_Product = request.getParameter("p_Product");
String v_Accounts = request.getParameter("p_Accounts");
String v_Scenario = request.getParameter("p_Scenario");
String v_Year = request.getParameter("p_Year");
String v_Value = request.getParameter("p_Value");
IEssGridView grid = cv.getGridView();
grid.setSize(2, 5);
grid.setValue(0, 1, v_Market);
grid.setValue(0, 2, v_Product);
grid.setValue(0, 3, v_Accounts); ;
grid.setValue(0, 4, v_Scenario);
grid.setValue(1, 0, v_Year);
cv.performOperation(cv.createIEssOpRetrieve());
System.out.println("\nData Cell at 2nd-row, 2nd-column: " + grid.getValue(1,1).toString());
System.out.println ("Market: "+v_Market+" Product: "+v_Product+" Accounts: "+v_Accounts+" Scenario: "+v_Scenario+" Year: "+v_Year+" Value: "+v_Value);
int row = 1, col = 1;
if (grid.getCellContentType(row, col) ==
IEssGridView.CELL_CONTENT_TYPE_DOUBLE) {
IEssValueAny val = grid.getValue(row, col);
double dblVal = val.getDouble();
grid.setValue(row, col, Double.valueOf(v_Value).doubleValue());
} else if (grid.getCellContentType(row, col) ==
IEssGridView.CELL_CONTENT_TYPE_MISSING) {
grid.setValue(row, col, Double.valueOf(v_Value).doubleValue());
}
IEssOpUpdate opUpd = cv.createIEssOpUpdate();
cv.performOperation(opUpd);
}catch (EssException x){
System.out.println("ERROR: " + x.getMessage());
}
%>
<%="WriteBack Ended" %>
<%="WriteBack Ended" %>
<%
//response.sendRedirect("http://localhost:9704/analytics");
%>After compiling the above jsp, deploy this to any Java Application server as an EAR file. The main reason for doing this is to have a URL that we can call using the UTL_HTTP database package. If more security is needed, one can code them directly into the JSP so that no one else is able to access the jsp outside of the UTL_HTTP package.

The next step is to create the Global Temporary Table. The structure of the Global temporary table can contain any number of columns. But we would need a column which we would be inserting into through the template via a function. In my case the Global Temporary table contains all the write back columns as well as an extra column that indicates whether the write back was successful or not.
create global temporary table EssbaseWriteBack_GTT(Year varchar2(100),Market varchar2(100),Product varchar2(100), Scenario varchar2(100), Sales Number, WriteBackStatus Number ) ON COMMIT DELETE ROWS;
Once the global temporary table has been created, we need to create a function which will basically pass the input parameters to the JSP. The JSP is basically called through the UTL_HTTP package and the parameters are passed using the GET method. If you need more security, POST method can also be used.The idea is for every row insert, the row attributes are passed into this function which would basically write back into Essbase.
create or replaceFUNCTION WriteBack_GTT(p_Year varchar2,p_Market varchar2,p_Product varchar2,p_Scenario varchar2, p_value NUMBER ) RETURN NUMBER IS req Utl_Http.Req; resp Utl_Http.Resp; v_msg varchar2(80); v_url varchar2(32767) := 'http://localhost:9704/AllocEssbase-AllocEssbase-context-root/EssbaseWriteback.jsp?'; begin v_url := 'http://localhost:9704/AllocEssbase-AllocEssbase-context-root/EssbaseWriteback.jsp?'; v_url := v_url||'p_Market='||p_Market||'&p_Year='||p_Year||'&p_Accounts=Sales&p_Scenario='||p_Scenario||'&p_Product='||p_Product||'&p_Value='||to_char(p_Value); Utl_Http.Set_Response_Error_Check ( enable => true ); Utl_Http.Set_Detailed_Excp_Support ( enable => true ); req := Utl_Http.Begin_Request ( url => v_url, method => 'GET' ); Utl_Http.Set_Header ( r => req, name => 'User-Agent', value => 'Mozilla/4.0' ); resp := Utl_Http.Get_Response ( r => req ); Dbms_Output.Put_Line ( 'Status code: ' || resp.status_code ); Dbms_Output.Put_Line ( 'Reason phrase: ' || resp.reason_phrase ); Utl_Http.End_Response ( r => resp ); RETURN 1; exception when Utl_Http.Request_Failed then Dbms_Output.Put_Line ( 'Request_Failed: ' || Utl_Http.Get_Detailed_Sqlerrm ); RETURN 0; when Utl_Http.Http_Server_Error then Dbms_Output.Put_Line ( 'Http_Server_Error: ' || Utl_Http.Get_Detailed_Sqlerrm ); RETURN 0; when Utl_Http.Http_Client_Error then Dbms_Output.Put_Line ( 'Http_Client_Error: ' || Utl_Http.Get_Detailed_Sqlerrm ); RETURN 0; when others then Dbms_Output.Put_Line (SQLERRM); RETURN 0; end;
The next step is to create the Write back template as shown below.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?><WebMessageTables xmlns:sawm="com.siebel.analytics.web/message/v1"><WebMessageTable lang="en-us" system="WriteBack" table="Messages"><WebMessage name="WriteBack"><XML>
<writeBack connectionPool="SH">
<insert> </insert>
<update>INSERT INTO EssbaseWriteBack_GTT(YEAR,MARKET,PRODUCT,SCENARIO,Sales,WRITEBACKSTATUS)
VALUES ('@{c0}','@{c1}','@{c2}','@{c3}', @{c4}, WriteBack_GTT('@{c0}','@{c1}','@{c2}','@{c3}', @{c4})) </update>
</writeBack>
</XML>
</WebMessage>
</WebMessageTable>
</WebMessageTables>
Place the write back template in the {OracleBI}\web\msgdb\customMessages folder. Restart the presentation services. Now navigate to the report and enable write back on the Sales column.

Once the write back is enabled, you should be able to update multiple rows back to Essbase simultaneously.


The above will work if you are on a Block storage cube(BSO). If you are on an Aggregate Storage(ASO) cube, you need to ensure that you are writing back only to level-0 intersections. Else the write back will fail. The other option for ASO cubes is to setup the write back partition with a BSO cube. The above architecture can even be expanded further to update cell comments, dimension members etc.